Digital transformation (DT) is a trendy subject in software development, despite the absence of a uniquely accepted definition of this concept. There are several ways of looking at it, depending on whether you’re leaning towards the macro or microeconomic side of the subject.
The World Economic Forum often references digital transformation in the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, implying the set of practices, goals, and management strategies to drive organizational changes with the help of digital technologies.
Business organizations tend to look at it from the practical view, meaning digitalization and automation of business processes.
Among the first companies to introduce the concept of digital transformation was a consulting company Capgemini. They defined DT as “the use of technology to radically improve performance or reach of enterprises”. That is a rather broad definition that we’re going to stick to for the purpose of this article.
Digital Transformation Technologies
Evaluating the far and wide consequences of DT is no easy task. DT is an umbrella term that includes a plethora of various digital technologies. Here is the display of some of them:
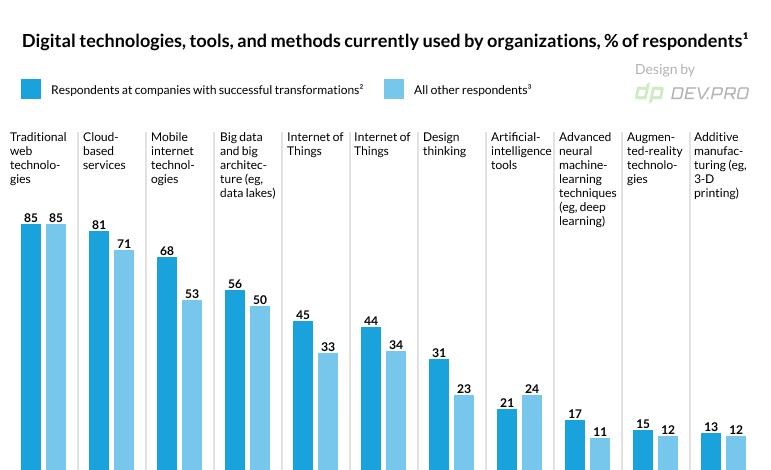
The research by McKinsey lists web, cloud, mobile, Big Data, and Internet of Things (IoT) (please see Figure 1) among the top technologies that companies choose as a part of their DT strategy.
In Which Industries Does Digital Transformation Work Better?
The success of digital transformation efforts partially depends on the number of steps that need to be taken to perform DT. Some industries clearly have an edge on it since they have always relied on digital technologies more than others.
It can be debated as to how to rank those industries since there’s various research (such as McKinsey or BCG, to name a few) that propose slightly different takes on that matter. We’ve grouped several industries together to avoid controversies and give a balanced view in this regard.
First Group: High Success Rate DT Industries
The list of high success DT organizations tops financial service, technological, media, and telecommunication companies. Traditionally, those companies have relied on the use of digital technologies to improve their customer service. It shouldn’t come as a surprise that embracing DT isn´t just as much of a challenge for them, resulting in a higher success rate.
Financial service typically includes commercial banks, alternative lending, investment, and insurance companies. These companies can leverage DT technologies in various ways.
Alternative lending, investment, and insurance companies score applications, based on multiple factors. Processing such applications manually can be extremely time-consuming, so artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies can speed up the process significantly.
Banks have lately been concerned with battling legacy IT systems, hence there’s a noticeable trend of moving IT infrastructure to the Cloud in the banking industry. The cloud migration requires fewer maintenance efforts and allows banks to focus more on the core banking activities.
The insurance industry used to be somewhat resistant to DT because of specific regulations in place. As regulations started getting relaxed, the industry opened up for new digital possibilities. In addition to the aforementioned IoT, AI, and ML, the insurance industry has been adopting blockchain technologies a lot lately.
When it comes to media and telecommunication, streaming services are on the rise. Companies like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, or Disney+ leverage software-as-a-service to revolutionize the way users consume video content. Here is how: cloud technologies allow people to watch movies regardless of the device they are using; the ML algorithm suggests next shows for watching, based on consumers’ previous behavior patterns.
Second Group: Average Success Rate DT Industries
The second group marks industries with the average success rate of DT, such as healthcare, automotive, logistics, and insurance. The need for DT here drives increasing client demands for a better digital experience.
The healthcare industry has seen an influx of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. The IoT wearable devices have made a noticeable shift in the medical industry. Remote blood pressure and glucose level monitoring, fall detection, and connective imaging are just a few examples of what the IoT has to offer.
It’s hard to point out any specific technology that made a noticeable effect on the automotive industry. It’s rather a combination of all-encompassing automation, connectivity, and electrification solutions that have Big Data, AI, ML, and even augmented reality (AR) technologies under the hood.
In the logistics industry, there’s a great deal of analytics, data visualization, and predictive modeling involved. Location-based services along with the IoT and Big Data are used to achieve the desired DT outcomes.
Third Group: Low Success Rate DT Industries
The third group is represented by the energy, public sector, industrial goods, and oil and gas industries. The low success rate for these businesses can be partially explained by the absence of a clear driving force to pursue digital transformation efforts.
The energy industry has tried implementing several IoT concepts, including smart meters and smart grids. However, these approaches have raised several security concerns and developing a smart grid is still in the concept phasel.
There’s little data to p the success of DT in the public sector. Most government projects related to DT deal with public health, cyberterrorism, and other subjects of national security, meaning that information is hard to come by. Some have suggested that the absence of competition in the public sector is what makes it relatively slow on embracing DT, especially compared to privately-owned tech companies.
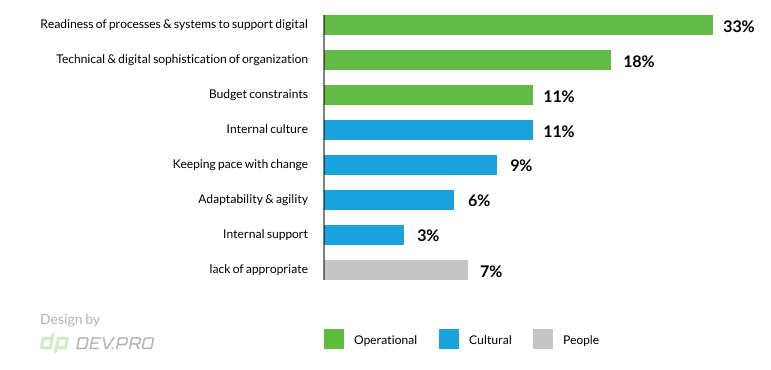
It took a while for industrial companies to realize DT is no longer just an option. Some industrial companies are known for having a few lifetime B2B clients and therefore might see little need for change. However, even the most conservative customers start to demand a better digital experience over time. Below are the main DT impediments for industrial companies (please see Figure 2).
Oil and gas companies face constantly increasing environmental protection requirements. Maintaining an effective production process under these conditions clearly indicates a need for digital transformation, according to BCG.
Digital Transformation Challenges and Risks
After covering the best-suited industries for digital transformation in the previous section, it would be safe to assume that second and third industry groups are the ones that face the most challenges and risks in the process.
A quick recap: the second group of companies deal with intense client pressure, while the third group is concerned with the absence of a clearly established motive.
Client pressure can result in the need to make changes quickly, sometimes without proper planning. This can lead to the following challenges and risks.
Insufficient Data Processing
Any decision related to digital transformation shouldn’t be taken lightly. Making an informed and evaluated solution requires a decent amount of customer data. Ironically, most companies are overwhelmed with client data: they just don’t know how to use it efficiently. That leads us to the next point.
Security Concerns
Nothing makes DT more challenging than the prospect of security implications. But it wouldn’t be fair to say that this is only a remote possibility. Poor judgment could lead to a poorly executed DT strategy, which could be a direct security threat.
Too Many Change Managers, but Few Change Enablers
In any organization, proposed changes are often met with a level of resistance. People fear the unknown, so be prepared for fierce objections. Nevertheless, important changes must be done, even if it means stepping out of the comfort zone for some organization members.
All in all, companies with an average success rate should plan their move carefully while companies with a low success rate should consider making changes to their organizational structure.
What Defines Success of Digital Transformation?
Digital maturity is the main factor that influences the success of a digital transformation (Figure 3).
Other factors, like clearly established priorities, thorough progress monitoring, and the commitment of c-level executives play an important role along the way.
Where Should You Start with Your Digital Transformation?
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach, unfortunately. There’s a lot you can learn from the experience of other companies in your industry that have attempted digital transformation. But you can avoid failure by learning from their mistakes before attempting DT.
Don’t have time to figure it out on your own? Contact Dev.Pro to get help!