Blockchain use cases in healthcare are a common sight in 2022. For example, IBM’s Digital Health Pass solution serves as the basis for the COVID-19 Excelsior pass used in New York to attend concerts and sporting events. No private medical data is shared through the app, only proof of vaccination or test results in the form of a QR code.
According to IDC’s Worldwide Blockchain Spending Guide, the healthcare industry is expected to increase spending on blockchain at a 5-year CAGR of 49.3% between 2019 and 2024.
Deloitte’s 2020 Global Blockchain Survey states that 90% of senior executives agree that global digital identity will be very or somewhat important in their overall blockchain and digital asset strategies.
According to the Wall Street Journal, the U.S. will soon spend 20% of its GDP on healthcare — a higher per capita rate than any other country.
Why are there so many applications for this technology in a highly regulated realm like healthcare?
Blockchain and HealthTech: A Perfect Match
Why is blockchain technology a good fit for HealthTech products?
The technology is founded on three pillars: immutability, transparency, and security. Its records are unchangeable. Peer-to-peer transactions make the system transparent and its proof-of-work mechanism makes it incredibly secure.
For an industry like healthcare, which is full of regulations, compliance demands, and a host of personal information, blockchain is a perfect fit.
Let’s look at some examples of how blockchain technology can meet these needs in the healthcare sector.
What are the Use Cases of Blockchain in Healthcare?
The healthcare system is a complicated landscape with a multi-party network of interests, concerns, issues, and regulations:
- Patients should have the tools to keep their medical records safe and private, while maintaining their right to provide access to those records and share them to medical professionals. Naturally, private blockchains are used for extra security or meticulous data encryption is in place.
- Doctors and medical staff need patients’ full records to be able to offer the best course of treatment.
- Insurance companies need precise health data to provide the best coverage terms.
- Pharmaceutical industry needs access to health records of research participants to quickly test and produce medications.
- Governments and their enforcement authorities [like the FDA in the U.S.] need data to understand the population they serve in order to ensure healthcare coverage for the needy and introduce legislative initiatives to protect citizens.
Blockchain technology can transform healthcare and is the perfect tool for decentralized data storage and distribution. These are the top applications of the technology in this domain:
Use Case 1. Decentralized Storage of Patient Data
A patient’s Electronic Health Records [EHR] are a wealth of sensitive data. Currently, this data is usually stored in fragments, across different health service suppliers, private practices, and state medical institutions.
In the best case scenario, these medical data records are stored on on-premise servers or a private cloud. In the worst case scenario [which is likely the case for a majority of the global population], health records are kept in paper medical books on the shelf.
Global decentralized storage of medical data is one of the most far-reaching blockchain healthcare use cases.
Not only does the technology serve as a hub for decentralized, yet global, data storage, it also grants full control to the patient to determine which parties get access to those sensitive records.
These blockchain-friendly healthcare companies are pioneering the field of decentralized EHR / EMR record keeping:
BurstIQ
As one of the pioneers of chain use in healthcare, BurstIQ creates a number of products and initiatives with technologies like AI, ML, blockchain, and the cloud.
A recent project with RemediChain helps people who struggle to pay for medication get access to life-saving drugs. Users donate their unused, unopened medications through an app. The initiative also helps tackle the 3.5 million tons of medications that are thrown away every year.
But BurstIQ’s core product is EHR and patient data management software. The company addresses the dilemma of storing disparate masses of sensitive personal medical records while ensuring privacy and high-level security. A key feature of the platform is its elaborate consent service, which includes permission-based revocable data sharing features.
Doxper
This Indian healthcare startup was recently acquired by Meddo after raising almost $6 million.
Their team of developers created a product that allows doctors to use a digital pen and encoded paper technology to turn handwriting as typed text. The developers used blockchain technology for the product’s ecosystem. Data from patients and prescriptions made by doctors is processed, stored, and transmitted between parties on the blockchain.
Use Case 2. Drug Traceability In The Pharmaceutical Supply Chain
An estimated 10% of drugs on the market are counterfeit. It’s even a problem in the developed world, where 1% of drugs are estimated to be counterfeit.
IBM – FDA pilot project
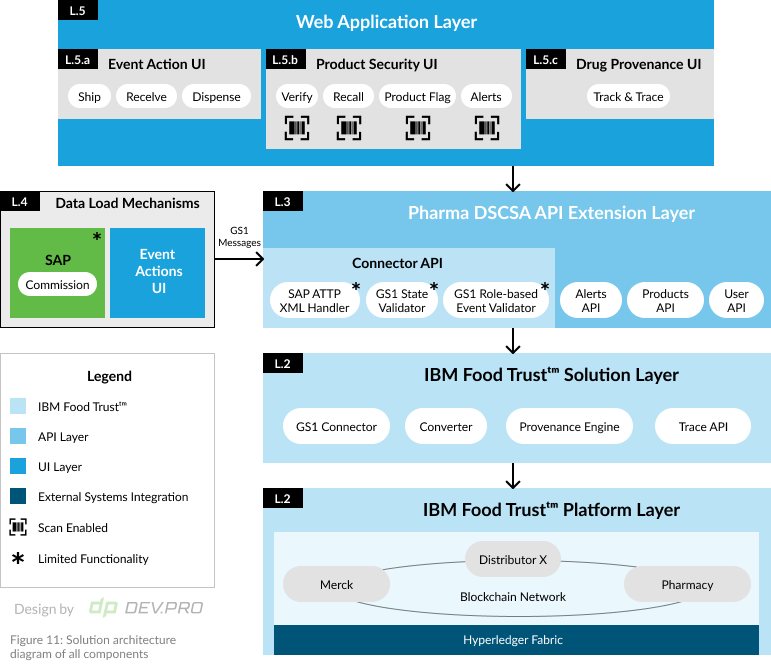
Drug traceability and pharmaceutical integrity were at the heart of the FDA pilot project run by IBM, Walmart, KPMG and Merck. The project was run in support of the U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act, which aims to make drug origin and authenticity transparent and traceable.
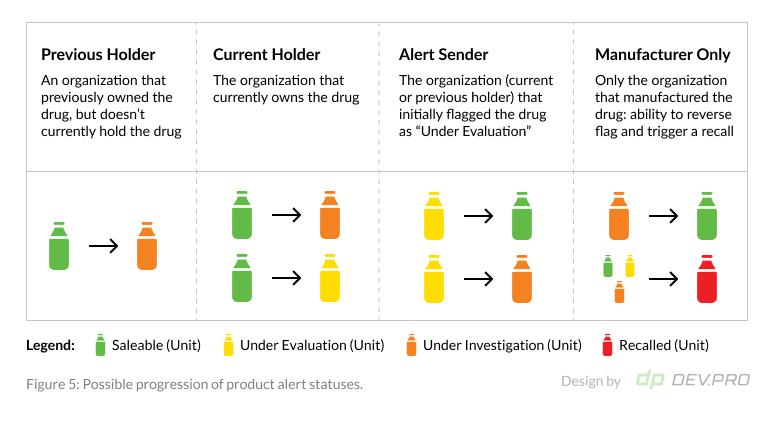
The goal of the project was to establish whether blockchain could be used to establish a common record of product logistics between ingredients supplier, manufacturers, distributors, re-packagers, pharmacy, and dispensers. The team also wanted to see if blockchain technology could help reinforce patient safety by enabling a product alert chain. Both of these objectives were successfully achieved.
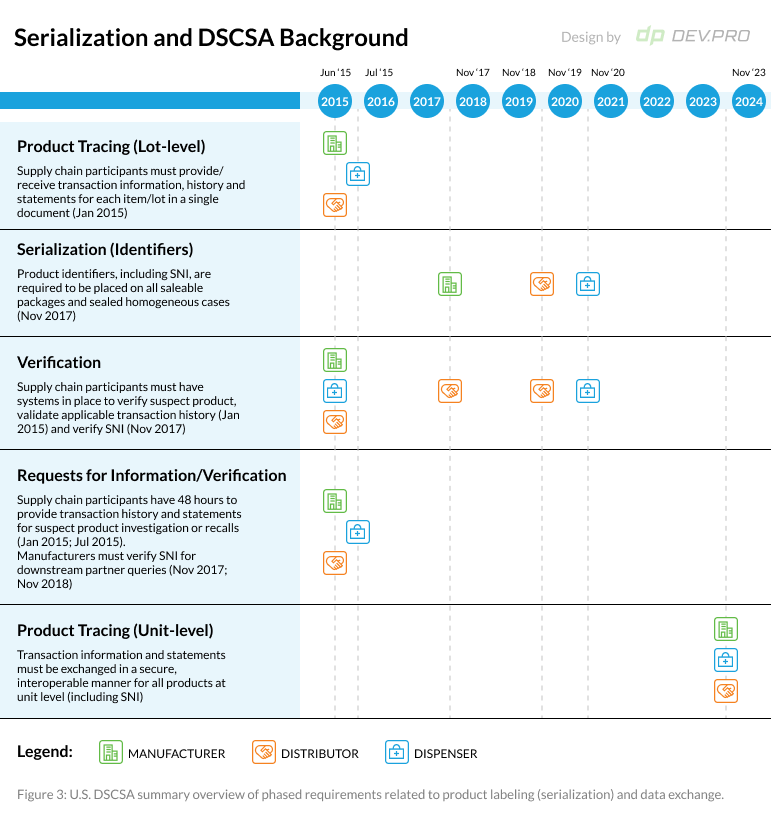
Figures 1-3 illustrate an architectural diagram of the solution, the progression of product alert statuses as they move along the chain of parties, and the product labeling roadmap.
Source: IMB
Chronicled
Chronicled developed the MediLedger Network based on blockchain technology. It helps healthcare providers with product verification, contract management, and claim adjudication. The network includes drug manufacturers and healthcare providers like Pfizer, Bayer, Genentech, Premier, and Cardinal Health.
This network of aligned industry master data includes a privacy-first design, roster management, and secure peer-to-peer messaging. The program is helping contribute to the creation of a safe and reliable drug supply chain.
Use Case 3. Tamper-Proof Patient Data
Medical records are a coveted possession for many parties in the health industry. Yet, it’s in the interest of the patient to keep data confidential.
This is where the smart contracts come in handy. They are the perfect tool for keeping EMR secure.
Moreover, the technology allows a patient to sell their data for scientific or analytical purposes.
Once the patient’s medical records are saved on the blockchain, the owner of the data gets a unique key. Their data only becomes accessible when they share this key.
One blockchain framework for accessing EHR based on multiple certificate authority [CA] has been elaborated at Monash University in Malaysia with support from Taif University in Saudi Arabia.
Medicalchain
Medicalchain is a major disruptor in the U.K. healthcare industry., It is pioneering the use of blockchain technology to store patient data and medical records on a blockchain. Dr Albeyatti, the founder and CEO of the company, says that “blockchain … is the most secure way to carry around this technology. Essentially, it is a distributed ledger that can’t be corrupted or changed without disrupting the chain in that process. So if somebody tried to change a clinic letter, that corruption at that specific place would be flagged.”
The company also hopes to grant access and revoke rights to patients in a bid to create the environment where it’s up to patients to manage of their medical records in a safe manner.
Use Case 4. Encryption and Security of PHI
Only 63% of healthcare organizations encrypt Protected Health Information [PHI] on their digital devices, despite strict HIPAA encryption requirements in the US market, for example.
Mobile devices, laptops, servers, emails, and EMR systems all need to be encrypted to ensure hackers don’t take advantage of the sensitive PHI they contain.
The best practice is to use AES-256, AES-128, or Triple DES encryption. This is where blockchain technology can help life science and healthcare systems. See how encryption gets an extra security layer with blockchain technology in the case below.
Testd
Testd is a leading U.S. medical tests and vaccine verification platform that uses blockchain technology to encrypt PHI. Testd’s vaccination and testing data is further anonymized so that it’s harder to track and trace.
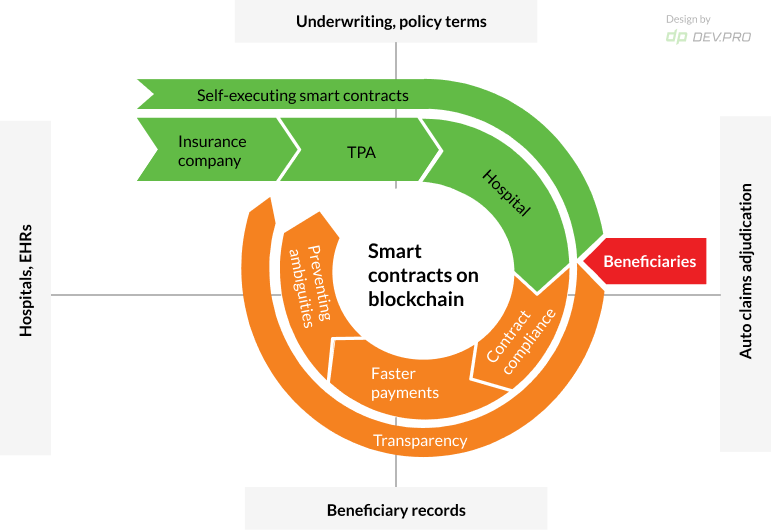
Use Case 5. Smart Contracts for Medical Claims Verification
Health insurance claim verification is another blockchain application in healthcare that can automate the process by making smart contracts part of the decision-making process.
Fake health records, fake identities and fraudulent claims are just a few of the issues faced by insurance companies, TPAs, and hospitals. Patients, on the other hand, face a 17% chance of in-network claims being denied due to reasons like service not being covered, a claimant not enrolled, incomplete information, or a duplicate claim.
Due to its distributed and decentralized nature, self-executing smart contracts can address and prevent pain points for hospitals, insurance companies, patients, and TPAs. Both underwriting and claims processing can be performed using self-executing smart contracts.
The main concerns that arise when discussing verification of medical claims via smart contracts include the potential for exponential growth in the number of transitions and respective cost of maintenance, as well as the quality of the input, whereby “garbage in garbage out” is true in the blockchain environment.

Source
Source
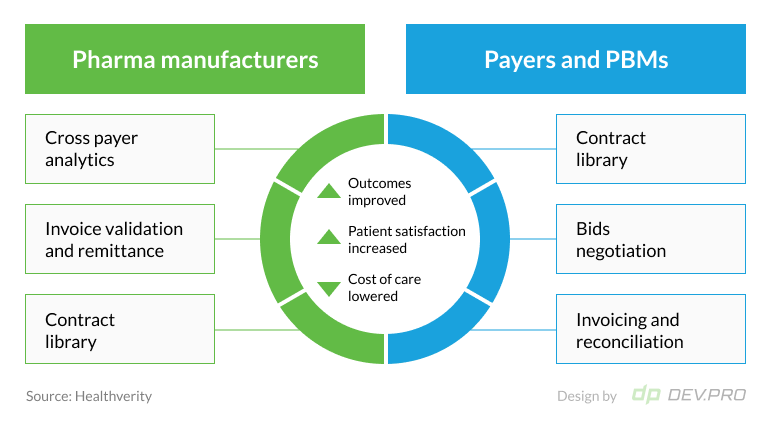
Healthverity
After raising $142 million over four rounds, Healthverity is set to transform the healthcare industry through a number of HealthTech software solutions, many of them based on blockchain technology.
Contract and rebate management is one of the company’s focuses. It aims to facilitate and customize the collaboration process between the parties on both ends of the healthcare provisioning process.
Source: Healthverity
Benefits of Using Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain technology’s main benefit is that it’s immutable and tamper-proof, which makes it valuable for health insurance claims underwriting and HPI safekeeping.
Security is another valued asset — a consensus system is used to verify any changes, meaning that the system is secured at multiple points..
Fraud protection is embedded in the blockchain’s traceable infrastructure.
Moreover, the transaction cost of smart contract initiation and maintenance is usually lower than the commission of mediators.
What is the Future of Blockchain in Healthcare?
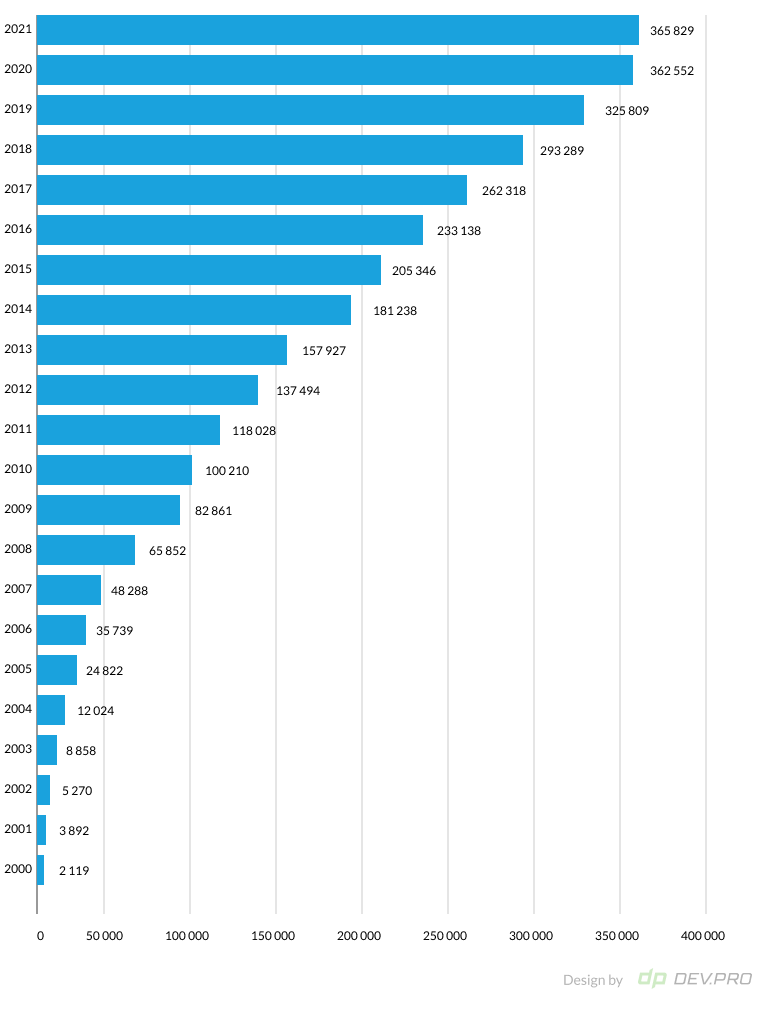
To illustrate the exponential growth in the life science and healthcare sectors, let’s look at the number of registered clinical trials worldwide for the past two decades. From just 2,119 clinical trials run in 2000, the pharmaceutical industry grew to running 362,000 trials in 2020.
Source
Needless to say, blockchain technology’s multiple advantages will continue to advance the decentralization of healthcare. From HPI safekeeping, medical insurance processing, telehealth, to data exchange for research and trials, decentralization is here to stay.
Looking for a software development company with blockchain experience to drive your healthcare project?
DevPro’s software engineers have worked on several blockchain software development projects, including recent projects with Inveniam, Securrency, and Coinsquare.
Schedule a 15 minute call with our sales team to discuss how our blockchain expertise can help you become a trendsetter in healthcare tech.